Comparing Gravity Casting and Die Casting: Choosing the Right Metal Casting Process
2024-06-11
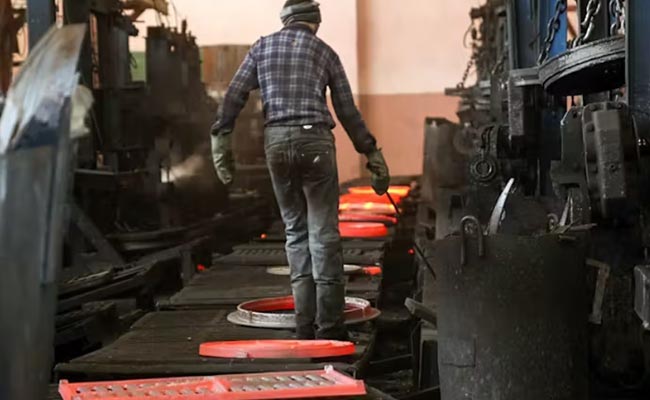
How casting mold is being made
2024-06-24Innovation often leads to efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and enhanced product quality. One such innovation that is reshaping the landscape of casting processes is the utilization of 3D printed molds. By harnessing the capabilities of additive manufacturing, industries are unlocking new possibilities in casting production, paving the way for faster turnaround times, intricate designs, and reduced tooling costs.
The Traditional Casting Process
Traditionally, casting involves the creation of a mold, typically made of sand, plaster, or metal, into which molten material is poured to create a desired shape. While this process has been used for centuries and remains widely employed today, it often comes with limitations in terms of design complexity, tooling requirements, and production time.
Enter 3D Printed Molds
The advent of 3D printing technology has revolutionized the way molds are produced for casting applications. Instead of relying on traditional mold-making techniques, manufacturers can now utilize 3D printers to directly fabricate intricate mold designs layer by layer from digital models. This approach offers several significant advantages:
Design Freedom: With 3D printing, virtually any complex geometry can be translated into a mold design without the constraints of traditional manufacturing methods. This opens up new possibilities for creating intricate and customized castings that were previously impractical or impossible to achieve.
Rapid Prototyping: 3D printing enables rapid prototyping of molds, allowing designers and engineers to iterate on designs quickly and cost-effectively. This accelerated design cycle reduces time to market and facilitates product development and optimization.
Cost Efficiency: Traditional mold-making processes often require the fabrication of expensive tooling, which can be a significant upfront investment, especially for small production runs. In contrast, 3D printed molds eliminate the need for tooling, resulting in lower setup costs and making casting more accessible to a wider range of applications and industries.
Customization: 3D printing allows for on-demand production of molds tailored to specific casting requirements. This enables manufacturers to produce customized parts with unique features or variations without incurring additional tooling expenses.
Improved Accuracy and Consistency: The precision and repeatability of 3D printing technology ensure consistent mold quality and dimensional accuracy, leading to high-quality castings with minimal defects.
Applications of 3D Printed Molds in Casting
The versatility of 3D printed molds has led to their adoption across various casting processes and industries, including:
Investment Casting: 3D printed molds are ideal for investment casting applications, where intricate and highly detailed parts are required. The ability to create precise and intricate molds facilitates the production of complex components for aerospace, automotive, and medical applications.
Sand Casting: In sand casting, 3D printed sand molds offer advantages in terms of design flexibility, rapid prototyping, and cost-effectiveness. They are used in the production of a wide range of parts, from automotive components to architectural elements.
Permanent Mold Casting: 3D printed metal molds can be used in permanent mold casting processes, such as gravity die casting and low-pressure casting, to produce high-quality metal parts with improved dimensional accuracy and surface finish.
Prototype Casting: For rapid prototyping and low-volume production, 3D printed molds provide a cost-effective solution for producing functional prototypes and short production runs without the need for expensive tooling.
Challenges and Future Directions
While 3D printed molds offer numerous benefits, they also present challenges, such as material limitations, surface finish considerations, and post-processing requirements. However, ongoing advancements in materials science, process optimization, and digital design tools are addressing these challenges and expanding the capabilities of 3D printed molds in casting applications.
As the technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see further integration of 3D printing into casting processes, driving innovation, and enabling new possibilities in product design, manufacturing, and supply chain management. With its ability to revolutionize traditional casting methods, 3D printed molds are poised to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of manufacturing across industries.