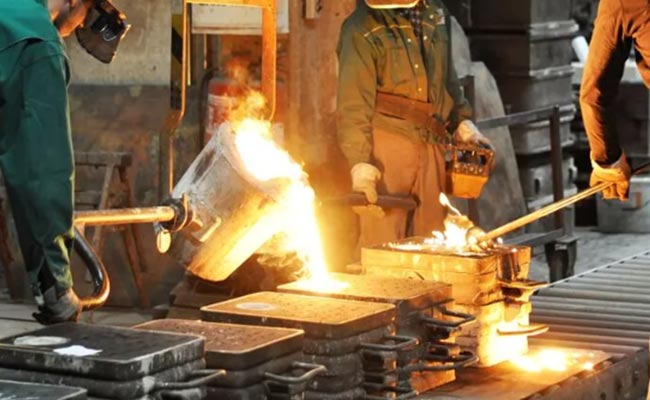
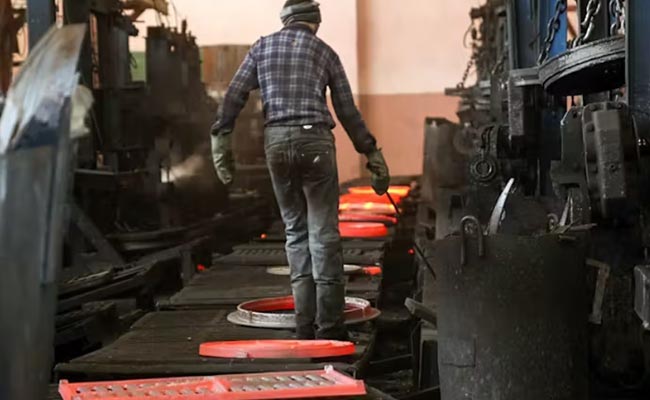
What Is The Heat Treatment Of Gray Iron?
2021-11-26
Merry Christmas
2021-12-24
1. Cast carbon steel. Cast steel with carbon as the main alloying element and a small amount of other elements. Cast carbon steel can be divided into cast low carbon steel, cast medium carbon steel and cast high carbon steel. The carbon content of cast low carbon steel is less than 0.25%, the carbon content of cast carbon steel is between 0.25% and 0.60%, and the carbon content of cast high carbon steel is between 0.6% and 3.0%. The strength and hardness of cast carbon steel increase with the increase of carbon content.
Cast carbon steel has the following advantages: lower production cost, higher strength, better toughness and higher plasticity.
Cast carbon steel can be used to manufacture parts that bear heavy loads, such as rolling mill stands and hydraulic press bases in heavy machinery. It can also be used to manufacture parts that are subject to great force and impact, such as wheels, couplers, bolsters and side frames on railway vehicles.
2. Cast alloy steel. Casting alloy steel can be divided into cast low alloy steel (the total alloy elements are less than or equal to 5%), cast alloy steel (the total alloy elements are between 5% and 10%) and cast high alloy steel (the total alloy elements are greater than or equal to 10%).
According to the characteristics of use
- Cast tool steel. Cast tool steel can be divided into casting tool steel and casting mold steel.
- Casting special steel. Casting special steel can be divided into cast stainless steel, cast heat-resistant steel, cast wear-resistant steel, cast nickel-based alloy and so on.
- Cast steel for engineering and structure. Cast steel for engineering and structure can be divided into cast carbon structural steel and cast alloy structural steel.
- 4. Cast alloy steel. It can be divided into cast low alloy steel, cast medium alloy steel and cast high alloy steel.