Preventive Measures for Common Defects of Ductile Iron
2021-09-18
Annealing of Steel
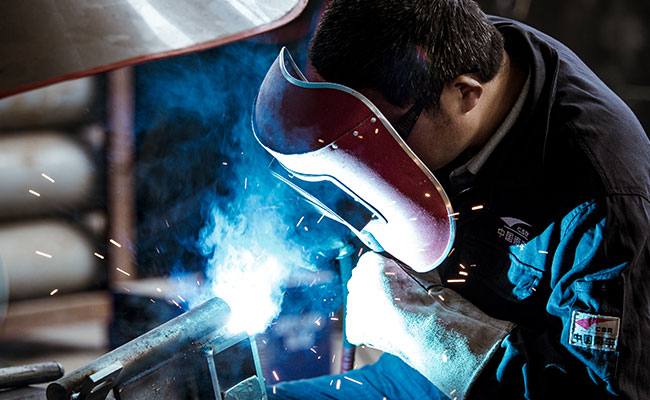
2021-10-08Due to the difference of heating method and melting method, welding has the following main types:
1. Gas welding
The gas mixture burns to form a high-temperature flame, which is used to melt the welding joints and electrodes. The most commonly used gas is a mixture of oxygen and acetylene. Adjusting the ratio of oxygen to acetylene can obtain oxidizing, neutral and reducing flames. The equipment used in this method is relatively simple, and the heating zone is wide, but the deformation of the weldment after welding is large, and the operation cost is high, so it is gradually replaced by arc welding.
2. Arc welding
This is the most widely used welding method. The main characteristics of arc welding are the formation of a stable arc, the supply of filler materials, and the protection and shielding of molten metal. Generally, the arc can be generated in two ways. In the first type, the arc occurs between a consumable metal electrode and the metal material. The electrode gradually melts during the welding process, thereby providing the necessary filler material to fill the joint. The second type: The arc occurs between the workpiece material and a non-consumable tungsten electrode. The melting point of the tungsten electrode should be higher than the arc temperature, and the necessary filling materials must be provided separately.
3. Electroslag welding
It uses the resistance heat generated by the electric current through the slag to melt the metal. The range of this kind of heat source is larger than that of an electric arc, and each welding wire can be formed into a circuit separately, increasing the number of welding wires, and can weld very thick weldments at one time.
4. Vacuum electron beam welding
This is a special welding method, used to weld small parts with high melting point and active metal in cutting-edge technology. Its characteristic is that the weldment is placed in a high-vacuum container, which is equipped with an electron gun, and uses high-speed electron beams to strike the weldment to melt the weldment for welding. This method can obtain high-quality weldments.
5. Laser welding
This is also a special welding method. It is a welding method that uses a focused laser beam as the energy source to bombard the weldment with the heat generated.
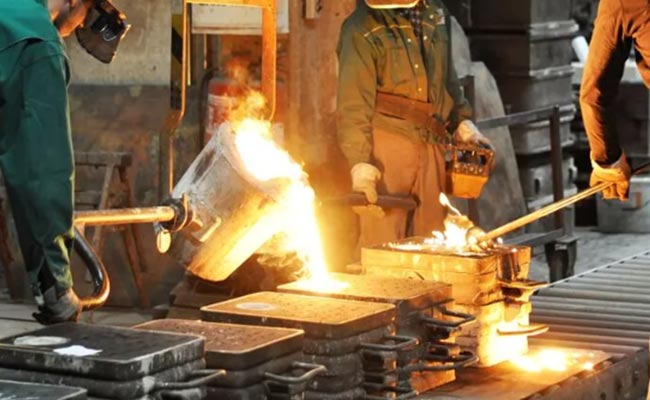
Due to different heating methods, pressure welding can have the following main types:
1. Resistance welding
This is the method of using resistance heating, the most commonly used are electric welding, seam welding and resistance butt welding. The first two are to heat the weldment to a partial melting state and pressurize at the same time. Resistance butt welding is to locally heat the weldment to a high plastic state or surface melting state, and then apply pressure. Resistance welding is characterized by a high degree of mechanization and automation, so the productivity is high, but it requires a strong current.
2. Friction welding
The friction heat is used to heat the contact surface to a high plastic state, and then pressure is applied to the welding. Since the oxide on the welding surface can be removed during friction, and the heat is concentrated on the welding surface, it is especially suitable for non-ferrous metals with good thermal conductivity and easy oxidation. Welding.
3. Cold pressure welding
The characteristic of this method is that it does not heat and only relies on strong pressure for welding. It is suitable for welding of base materials with lower melting points, such as lead wires, aluminum wires, and copper wires.
4. Ultrasonic welding
It is also a kind of cold pressure welding. With the help of ultrasonic mechanical oscillation, the required pressure can be reduced. At present, it is only suitable for spot welding of thin plates of non-ferrous metals and their alloys.
5. Diffusion welding
Diffusion welding is a welding method in which the weldments are tightly attached, in a vacuum or protective atmosphere, at a certain temperature and pressure for a period of time, so that the atoms between the contact surfaces are mutually diffused to complete the welding. Diffusion welding is mainly used for welding fusion welding, brazing small, precise and complex weldments that are difficult to meet technical requirements.
During pressure welding, the pressure causes the protruding part of the contact surface to plastically deform, reducing the height of the protruding part and increasing the real contact area. Temperature recrystallizes the plastically deformed part and accelerates the diffusion of atoms. In addition, surface tension can also promote the reduction of the volume of the cavity on the contact surface. This heating pressure welding process is similar to the hot pressing sintering process in powder metallurgy. During cold press welding, although there is no heating, due to the inhomogeneity of plastic deformation, the heat released is limited to the part that is actually in contact, so there is also a heating effect.