Open Die Forging: A Versatile Metalworking Process
2024-08-26
Cold Forging: A Precision Metalworking Process
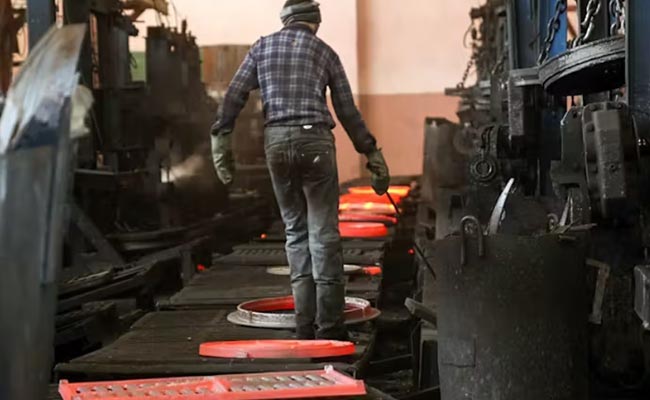
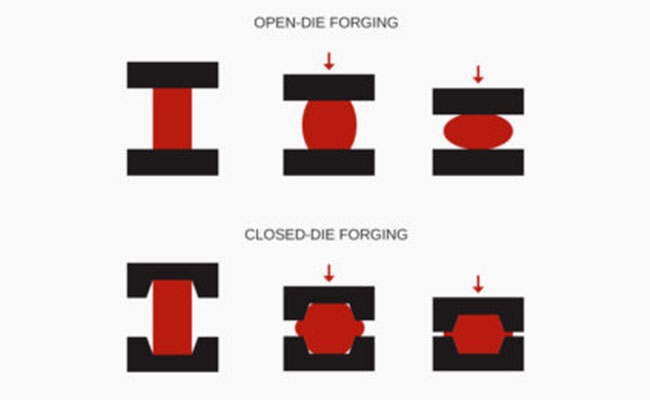
2024-09-09Closed die forging is a metalworking process that involves shaping a metal workpiece using compressive forces applied by a hammer or press within a closed die cavity. This process is used to produce a wide variety of parts, including automotive components, aerospace parts, and industrial machinery components. Closed die forging is a highly efficient and precise process that produces parts with excellent mechanical properties and dimensional accuracy.
Advantages of Closed Die Forging
High Production Rates: Closed die forging is a highly productive process that can produce large quantities of parts at a high rate.
Excellent Dimensional Accuracy: Closed die forged parts have excellent dimensional accuracy and consistency, which is critical for many applications.
Superior Mechanical Properties: The closed die forging process refines the grain structure of the metal, resulting in parts with superior strength, durability, and fatigue resistance.
Material Efficiency: Closed die forging is a highly efficient process that minimizes material waste.
Disadvantages of Closed Die Forging
High Tooling Costs: The dies used in closed die forging are expensive to design and manufacture.
Limited Design Flexibility: Closed die forging is best suited for parts with simple shapes and consistent geometries.
Part Complexity: Complex parts may require multiple forging operations, which can increase production costs.
Applications of Closed Die Forging
Automotive: Crankshafts, connecting rods, axles, and other high-strength components.
Aerospace: Landing gear components, turbine blades, and other critical parts.
Industrial Machinery: Gears, shafts, and other components that require high strength and durability.
Military: Armor plates, gun components, and other high-performance parts.
The Closed Die Forging Process
The closed die forging process typically involves the following steps:
Die Design and Manufacturing: The dies are designed and manufactured to produce the desired part shape.
Heating: The metal workpiece is heated to a specific temperature to make it malleable.
Forging: The heated workpiece is placed in the die cavity and shaped by the application of compressive force.
Trimming: Any excess material is trimmed from the forged part.
Heat Treatment: The forged part is often heat-treated to improve its mechanical properties.
Finishing: The forged part is finished to the desired dimensions and surface finish.
Types of Closed Die Forging
There are two main types of closed die forging:
Impression Die Forging: This process uses dies with a single impression to produce parts with a single shape.
Multiple Impression Die Forging: This process uses dies with multiple impressions to produce parts with complex shapes.