Closed Die Forging: Precision and Efficiency in Metalworking
2024-09-02
Rolled Forging: A Versatile and Efficient Process
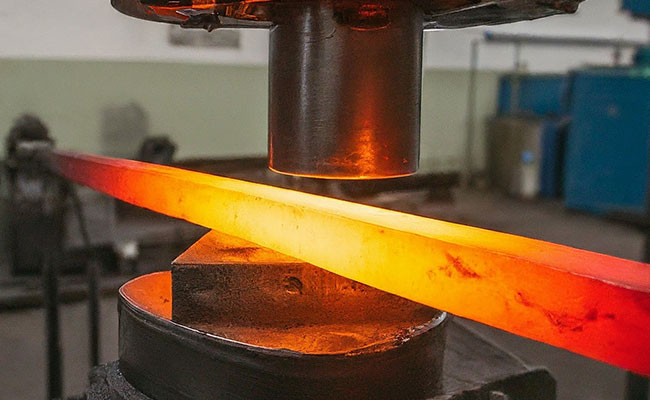
2024-09-18Cold forging, also known as cold heading, is a metalworking process that involves shaping metal at room temperature. It is a versatile process that can be used to produce a wide variety of products, from fasteners to automotive components. Cold forging is a cold working process, meaning that the metal is deformed without the application of heat. This results in a number of advantages over hot forging, including increased strength, improved dimensional accuracy, and a finer grain structure.
Advantages of Cold Forging
- Increased strength and durability: Cold forging strengthens the metal by refining the grain structure. This results in parts that are more resistant to wear and tear.
- Improved dimensional accuracy: Cold forging produces parts with tighter tolerances than hot forging. This is due to the fact that the metal does not expand and contract as it does in hot forging.
- Finer grain structure: The cold working process refines the grain structure of the metal, which results in a stronger and more durable part.
- Better surface finish: Cold forged parts have a better surface finish than hot forged parts. This is due to the fact that the metal is not exposed to the high temperatures used in hot forging.
- No need for post-processing: Cold forged parts often require less post-processing than hot forged parts. This is due to the fact that the parts are produced with a higher degree of accuracy.
Disadvantages of Cold Forging
- Limited to smaller parts: Cold forging is typically limited to smaller parts, as the metal becomes more difficult to deform as it gets larger.
- Higher tooling costs: Cold forging dies are typically more expensive than hot forging dies. This is due to the fact that the dies must be made with a higher degree of precision.
- More complex tooling: Cold forging dies are often more complex than hot forging dies. This is due to the fact that the metal must be deformed more gradually in cold forging.
Applications of Cold Forging
Cold forging is used to produce a wide variety of products, including:
- Fasteners: Bolts, nuts, screws, and rivets
- Automotive components: Crankshafts, connecting rods, axles, and gears
- Aerospace components: Landing gear components, turbine blades, and other high-strength parts
- Industrial machinery components: Shafts, gears, and other components that require high strength and durability
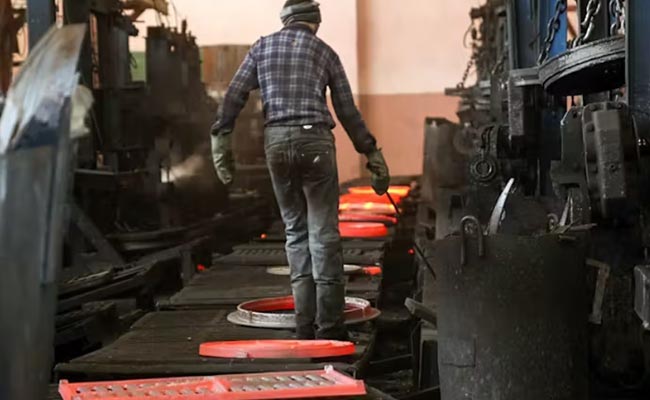
The Cold Forging Process
The cold forging process typically involves the following steps:
- Preparation: The metal is cut to the desired length and shape.
- Heating: The metal is heated to a specific temperature to make it more malleable.
- Forging: The metal is shaped using a series of dies.
- Trimming: Any excess material is trimmed from the part.
- Heat treatment: The part is often heat-treated to improve its mechanical properties.
- Finishing: The part is finished to the desired dimensions and surface finish.
Cold forging is a versatile and efficient process that can be used to produce a wide variety of high-quality products. While it does have some limitations, it is a valuable process for many applications.




