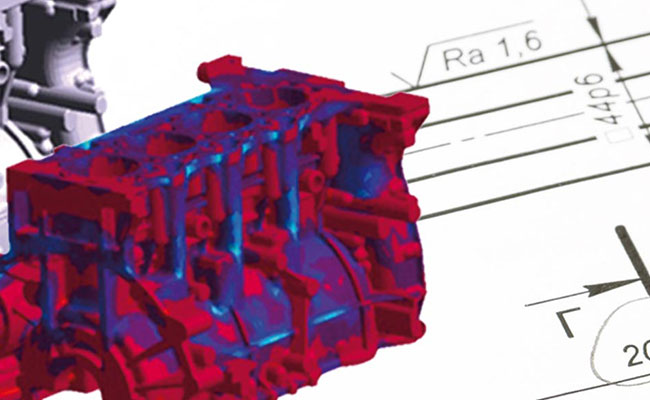
Pattern Creation in Casting
2025-03-12
5 NON-FERROUS METAL APPLICATIONS AND WHAT THEY’RE USED FOR
2025-03-24In casting, a prototype serves as a physical representation of the final product, allowing for testing and evaluation before full-scale production. Here are some common methods used for prototype creation in casting:
1. 3D Printing:
- Direct Printing: 3D printing can be used to directly create the prototype, especially for complex geometries or intricate designs. The prototype can then be used as a pattern for mold creation.
2. CNC Machining:
- Subtractive Manufacturing: CNC machining involves removing material from a solid block to create the desired shape. This method is suitable for prototypes with precise dimensions and complex features.
3. Casting:
- Investment Casting: Investment casting, also known as lost-wax casting, involves creating a wax model of the desired part, which is then used to create a mold for casting. This method can produce accurate prototypes with intricate details.
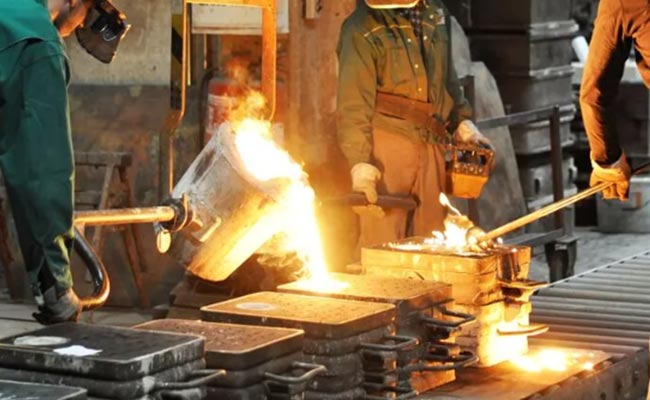
4. Sand Casting:
- Rapid Prototyping: Sand casting can be used to quickly create prototypes, especially for larger or more complex parts. This method involves creating a sand mold around a pattern, which is then used to cast the prototype.
5. Other Methods:
- Rapid Prototyping: Other rapid prototyping methods, such as stereolithography (SLA) and selective laser sintering (SLS), can be used to create prototypes quickly and efficiently. These methods are often used for complex geometries or when multiple iterations are needed.
Importance of Prototyping in Casting:
- Design Validation: Prototypes allow for testing and evaluation of the design before full-scale production, ensuring that the final product meets the desired specifications and performance requirements.
- Process Optimization: Prototypes can be used to optimize the casting process, such as identifying potential problems or areas for improvement.
- Cost Reduction: By identifying and addressing potential issues early on, prototyping can help to reduce costs and minimize production delays.
By using appropriate prototyping methods, manufacturers can ensure the quality, reliability, and efficiency of their casting processes.