Ultrasonic Testing (UT) for Castings
2024-10-14
Radiographic testing for Casting
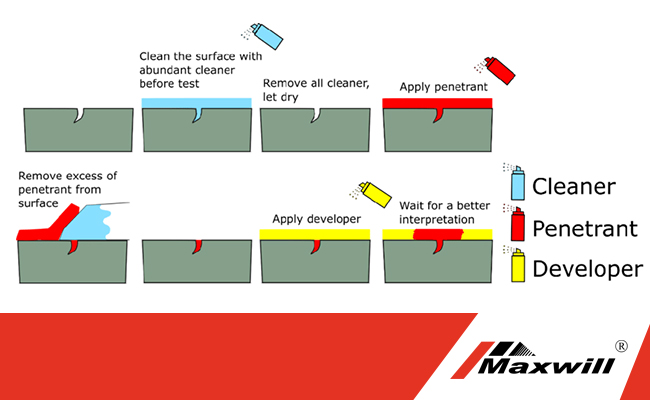
2024-10-28Liquid penetrant testing (PT) is a non-destructive testing (NDT) method used to detect surface-breaking discontinuities in castings. It involves applying a liquid penetrant to the surface of the casting, allowing the penetrant to seep into any surface-breaking cracks or discontinuities, and then revealing the penetrant using a developer.
How PT Works
- Cleaning: The casting surface is thoroughly cleaned to remove any dirt, oil, or grease that could interfere with the penetrant.
- Penetrant Application: A liquid penetrant is applied to the surface of the casting and allowed to penetrate into any surface-breaking discontinuities.
- Excess Removal: The excess penetrant is removed from the surface using a solvent or emulsifier.
- Developer Application: A developer is applied to the surface of the casting. The developer draws the penetrant out of the discontinuities, making them visible.
- Inspection: The surface of the casting is visually inspected for indications of penetrant seepage, which indicates the presence of a discontinuity.
Types of Penetrants
- Dye penetrants: Visible to the naked eye.
- Fluorescent penetrants: Require ultraviolet light to be seen.
- Water-washable penetrants: Removed with water, eliminating the need for solvents.
Advantages of PT for Castings
- Sensitivity: Can detect very small surface-breaking cracks.
- Portability: Portable PT kits are available for on-site inspections.
- Versatility: Applicable to a wide range of casting materials and shapes.
- Cost-effective: Relatively inexpensive compared to other NDT methods.
Limitations of PT for Castings
- Surface-breaking only: PT cannot detect internal flaws.
- Sensitivity to surface conditions: Rough surfaces or contaminants can interfere with penetrant penetration.
- Limited depth: PT is typically limited to detecting discontinuities near the surface.
- Operator skill: Accurate interpretation of PT results requires trained personnel.
Applications of PT in Casting
- Crack detection: Identifying surface-breaking cracks in castings.
- Porosity inspection: Detecting surface-breaking porosity.
- Inclusions: Finding surface-breaking inclusions in the casting material.
- Weld inspection: Assessing the quality of welds in castings.
In conclusion, liquid penetrant testing is a valuable tool for quality control in the casting industry. Its ability to detect surface-breaking discontinuities makes it an essential part of many casting inspection processes.