Non-Destructive Testing Methods for Casting Quality Control part 1
2025-05-12
Forging used in automobile industry
2025-05-266. Eddy Current Testing (ECT)
Purpose: Identifies surface and near-surface flaws in electrically conductive materials.
Process: Alternating currents are induced in the material, and variations in the current flow reveal defects.
Advantages:
Quick and portable.
Detects small cracks and corrosion.
Limitations:
Effective only for conductive materials.
Cannot detect deeper defects.
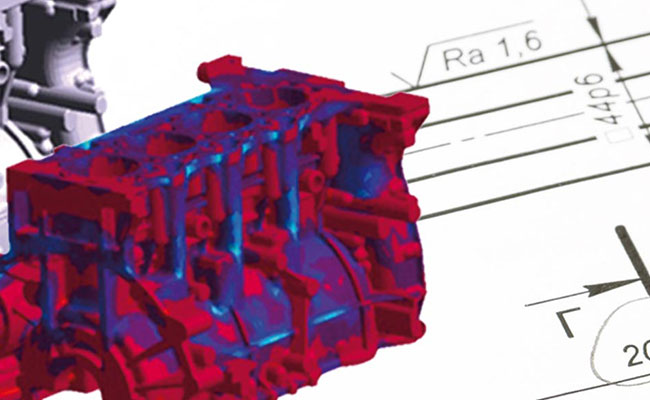
7. Computed Tomography (CT)
Purpose: Produces detailed 3D images of the internal structure of castings, revealing internal flaws and geometry deviations.
Process: X-rays are taken from multiple angles, and advanced algorithms create a 3D model of the casting.
Advantages:
Extremely precise and detailed inspection.
Useful for complex and high-precision castings.
Limitations:
Expensive and time-intensive.
Requires advanced expertise to interpret data.
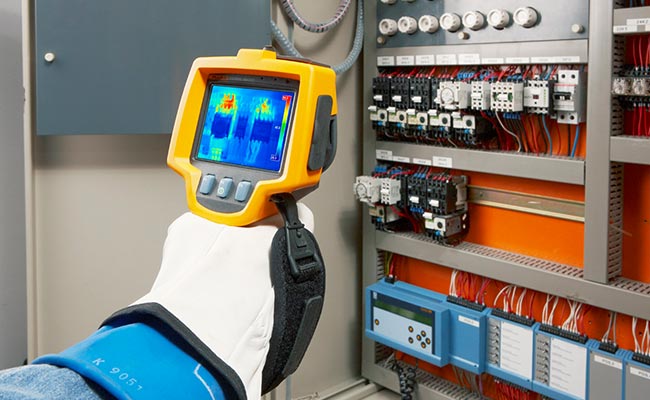
8. Thermographic Testing (TT)
Purpose: Detects subsurface defects by analyzing heat flow anomalies.
Process: The surface of the casting is heated or cooled, and infrared cameras detect variations in thermal conductivity caused by defects.
Advantages:
Non-contact method.
Can cover large areas quickly.
Limitations:
Limited to materials that exhibit significant thermal changes at defects.
Susceptible to environmental interference.
9. Resonance Testing (RT)
Purpose: Checks for structural integrity by analyzing the vibration or acoustic response of a casting.
Process: A known force is applied to the casting, and its response frequency is measured. Deviations indicate flaws.
Advantages:
Suitable for quick bulk testing.
Simple and cost-effective.
Limitations:
Limited accuracy for detecting specific defect types.
Requires reference data for comparison.
Factors in Choosing NDT Methods
The selection of the right NDT method depends on several factors:
Material: Ferrous, non-ferrous, conductive, or non-conductive.
Defect Type: Surface, subsurface, or internal.
Casting Complexity: Simple shapes vs. intricate geometries.
Budget and Resources: Availability of equipment and skilled technicians.
Conclusion
Non-destructive testing is an essential part of casting quality control, ensuring products meet specifications and are free from critical defects. By employing these techniques, foundries can improve customer confidence, reduce waste, and avoid costly recalls or failures. Advancements in NDT technologies are making inspections faster, more accurate, and more accessible, helping the casting industry align with modern standards and customer expectations.