Design for Manufacturability: 8 Tips to Optimize Cast Parts
2025-08-04
Recycling Metal Scrap: How Foundries Support Circular Economies Part Two
2025-08-18Recycling Metal Scrap: How Foundries Support Circular Economies Part One
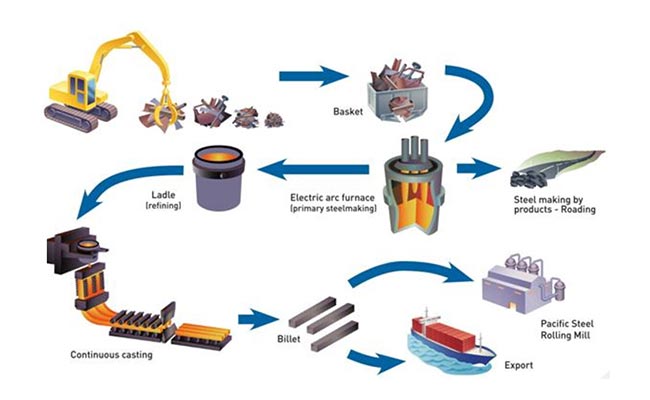
Recycling metal scrap is a crucial component of sustainable manufacturing and the circular economy. Foundries play a significant role in this process by transforming scrap metal into reusable materials, thereby reducing waste, conserving resources, and minimizing environmental impact. Here’s how foundries support circular economies through metal scrap recycling:
1. Collection and Sorting of Scrap Metal
Foundries often source scrap metal from industrial waste, end-of-life products, construction debris, and consumer goods.
Advanced sorting technologies, such as magnetic separators and eddy current systems, help separate different types of metals (e.g., ferrous and non-ferrous) to ensure efficient recycling.
2. Melting and Purification
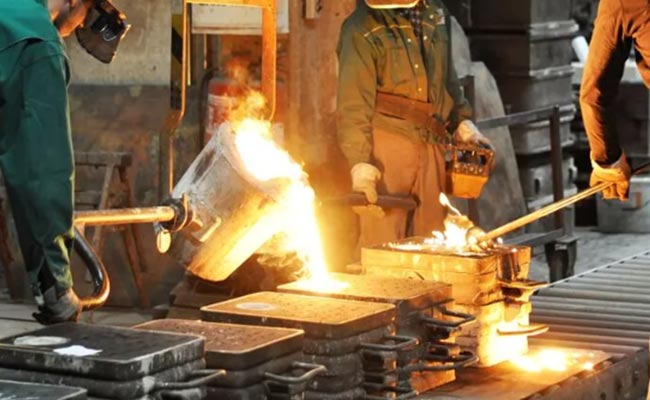
Scrap metal is melted in furnaces at high temperatures to remove impurities and create a homogeneous material.
Foundries use processes like refining and alloying to ensure the recycled metal meets specific quality standards for reuse in manufacturing.
3. Energy Efficiency and Emissions Reduction
Recycling metal scrap requires significantly less energy compared to producing metal from raw ore. For example, recycling aluminum saves up to 95% of the energy needed for primary production.
Foundries often adopt energy-efficient technologies and renewable energy sources to further reduce their carbon footprint.
4. Production of New Products
Recycled metal is used to manufacture new products, ranging from automotive parts and construction materials to consumer electronics and packaging.
This reduces the demand for virgin materials, conserving natural resources and minimizing environmental degradation from mining activities.
5. Waste Minimization
Foundries contribute to waste reduction by ensuring that metal scrap is reused rather than sent to landfills.
Byproducts of the recycling process, such as slag, can also be repurposed for construction materials or road building.