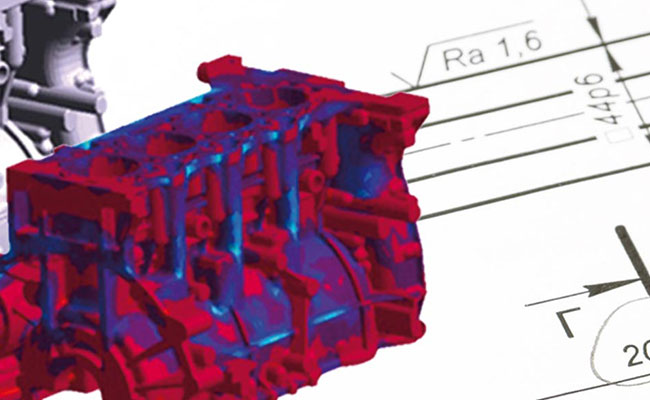
The Evolution of Die Casting: Precision for High-Volume Production
2025-06-03
Common Casting Defects: Porosity, Shrinkage, and More Part One
2025-06-16Ductile iron, also known as nodular cast iron, has become a material of choice for manufacturing durable, high-strength industrial components. Known for its superior mechanical properties, ductile iron has rapidly gained popularity in industries ranging from automotive to heavy machinery. But what exactly makes ductile iron such a standout material?
1. Exceptional Strength and Toughness
Ductile iron is lauded for its remarkable combination of strength, toughness, and flexibility. Its unique structure, where graphite is present in the form of small nodules, enhances its tensile strength compared to traditional cast iron. This makes it highly resistant to wear and impact—qualities that are especially important for parts subjected to high-stress environments. Ductile iron’s ability to absorb energy without fracturing is a significant advantage in industries requiring heavy-duty components.
2. Corrosion Resistance
One of the standout features of ductile iron is its excellent resistance to corrosion, particularly when exposed to harsh environments such as chemicals, moisture, and extreme temperatures. This resistance is a result of its dense microstructure and the graphite’s unique properties, which protect the material from rust and degradation. This durability makes ductile iron ideal for components like pipes, valves, and automotive parts that must endure long-term exposure to harsh conditions.
3. Cost-Effectiveness
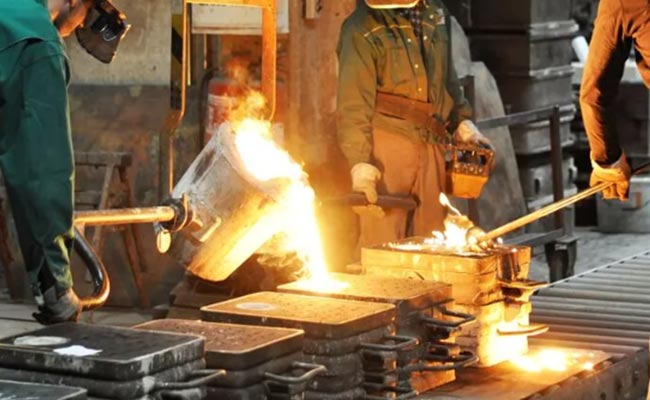
While ductile iron offers many of the benefits of steel, it’s often more cost-effective to produce. Its production process—typically involving casting—allows for complex shapes and intricate designs, reducing the need for additional machining or finishing. This makes ductile iron a practical choice for high-volume production of industrial components, offering both performance and value.
4. Versatility in Design and Application
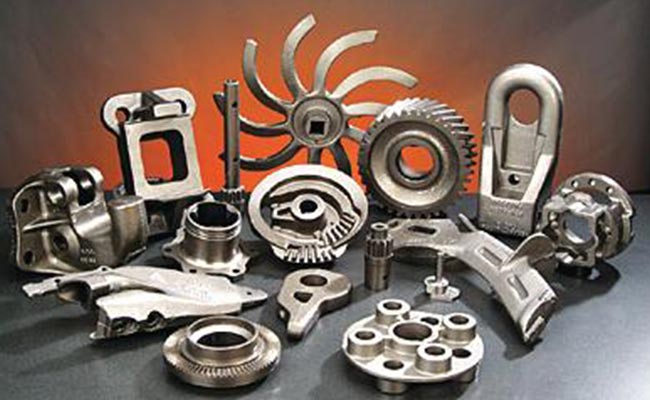
Another key benefit of ductile iron is its versatility. It can be cast into intricate shapes and sizes with high dimensional accuracy, which is crucial for producing parts that fit precisely in mechanical systems. This is especially valuable for industries like automotive manufacturing, where parts such as crankshafts, engine blocks, and suspension components must adhere to exact specifications to ensure performance.
5. Heat Resistance
Ductile iron also performs well under high-temperature conditions. Its ability to retain strength and resist thermal expansion makes it suitable for applications involving high heat, such as engine components, exhaust systems, and industrial machinery. This heat resistance extends the lifespan of parts and reduces the need for frequent replacements, saving costs in the long run.
6. Sustainable Manufacturing
With increasing emphasis on sustainability, ductile iron is becoming an increasingly attractive choice due to its recyclability. Scrap ductile iron can be melted down and reused to create new parts, minimizing waste and energy consumption during production. This aligns with modern manufacturing’s focus on green practices and the reduction of environmental impact.