Quality Inspection for Castings: Ensuring Product Excellence
2024-10-08
Liquid Penetrant Testing (PT) for Castings
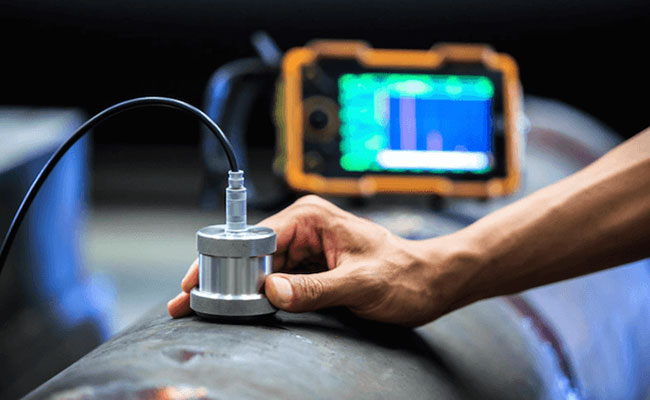
2024-10-21Ultrasonic testing (UT) is a non-destructive testing (NDT) method widely used in the casting industry to detect internal flaws and defects in castings. It utilizes high-frequency sound waves to penetrate the material and identify discontinuities such as cracks, voids, porosity, inclusions, and laminations.
How UT Works
- Transducer: An ultrasonic transducer, equipped with both a transmitter and receiver, is placed on the casting surface.
- Sound Wave Generation: The transducer emits high-frequency sound waves into the material.
- Wave Propagation: These sound waves travel through the casting, reflecting off any discontinuities or boundaries.
- Signal Analysis: The reflected signals are captured by the transducer and analyzed by a UT instrument.
- Flaw Detection: The presence and location of flaws are determined based on the characteristics of the reflected signals.
Types of UT Techniques for Castings
- Pulse-Echo: The most common technique, where the transducer acts as both a transmitter and receiver. Reflected echoes are analyzed to detect flaws.
- Through-Transmission: Two transducers are used, one as a transmitter and the other as a receiver. Flaws are detected by changes in the transmitted signal.
- Time-of-Flight Diffraction (TOFD): Used for detecting cracks and other discontinuities that are difficult to detect with other methods.
Advantages of UT for Castings
- Sensitivity: Can detect small flaws, including subsurface defects.
- Versatility: Applicable to a wide range of casting materials and shapes.
- Portability: Portable UT equipment allows for on-site inspections.
- Repeatability: Provides consistent and reliable results.
Limitations of UT for Castings
- Surface Roughness: Rough surfaces can interfere with the coupling of sound waves, affecting accuracy.
- Attenuation: Sound waves can be attenuated in certain materials, limiting penetration depth.
- Complex Geometries: UT can be challenging in castings with complex shapes or large variations in thickness.
- Operator Skill: Accurate interpretation of UT results requires trained personnel.
Applications of UT in Casting
- Defect Detection: Identifying cracks, porosity, inclusions, and other internal flaws.
- Thickness Measurement: Determining the thickness of castings.
- Material Characterization: Evaluating material properties, such as grain size and hardness.
- Weld Inspection: Assessing the quality of welds in castings.
In conclusion, ultrasonic testing is a valuable tool for quality control in the casting industry. Its ability to detect internal defects and provide accurate measurements makes it an essential part of many casting inspection processes.




